Anthracnose
Turf Disease
What Is Anthracnose?
Two forms of Anthracnose (Colletotrichum graminicola) frequently attack turf quality

Causal Agent: Colletotrichum cereale (Formerly Colletotrichum graminicola)
Susceptible Turfgrass: Annual bluegrass and creeping Bentgrass
Symptoms: Anthracnose is most destructive during warm weather. Making it one of the most common turf diseases in the UAE.
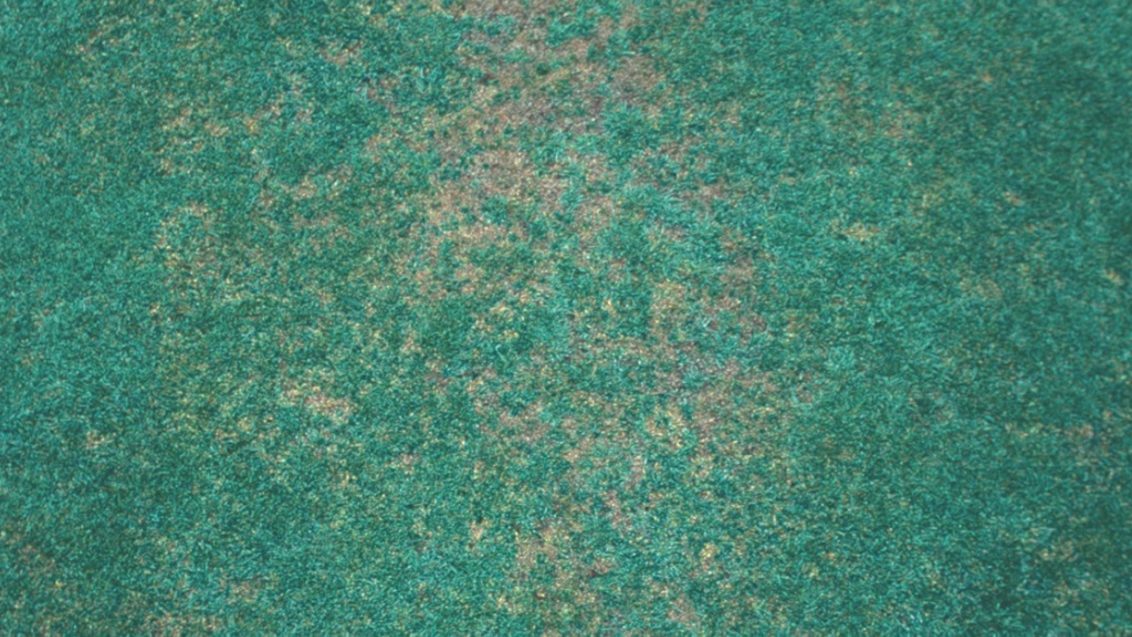
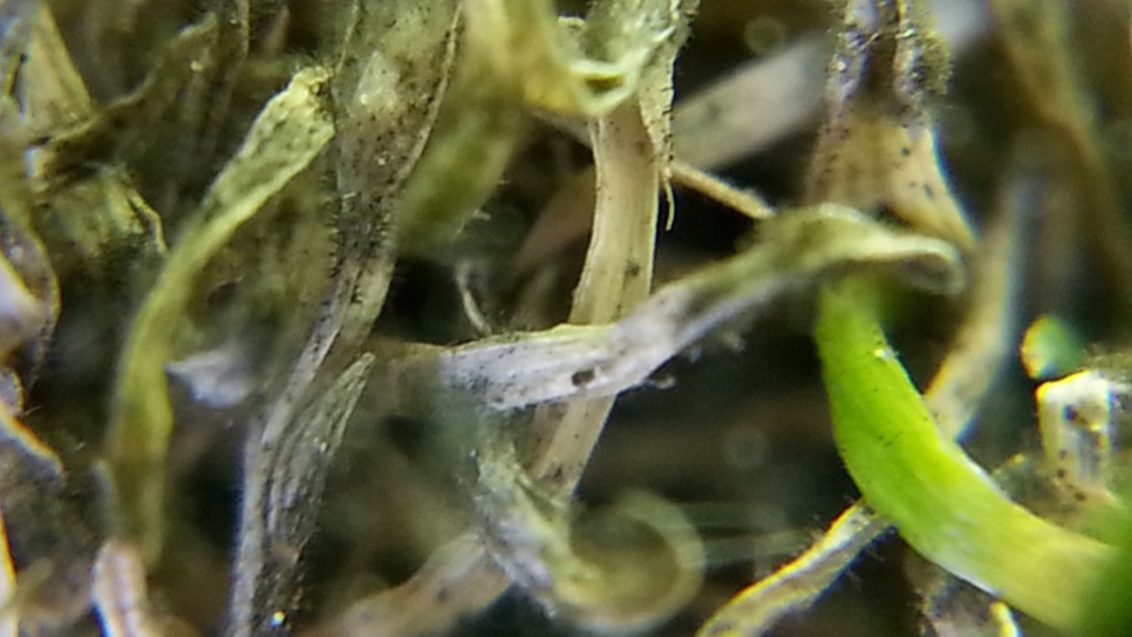
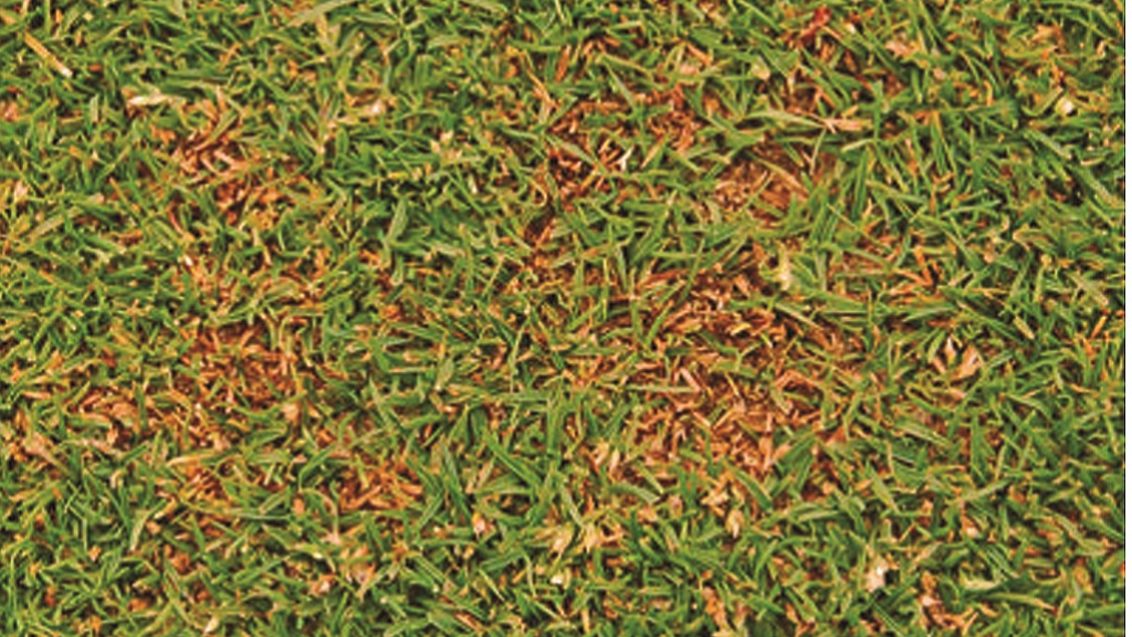
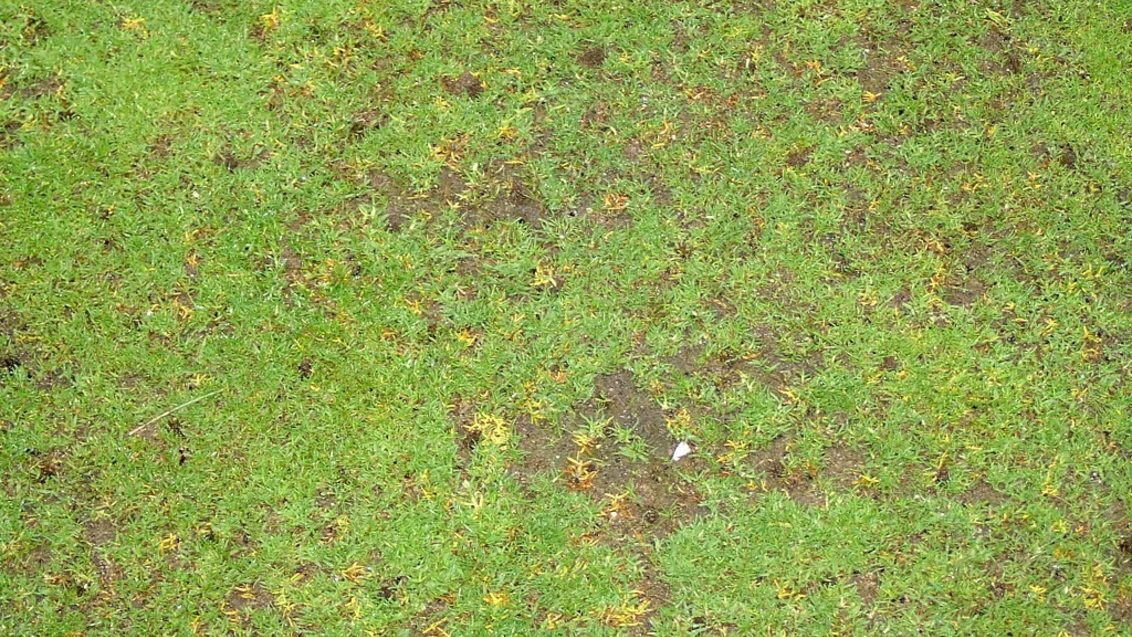
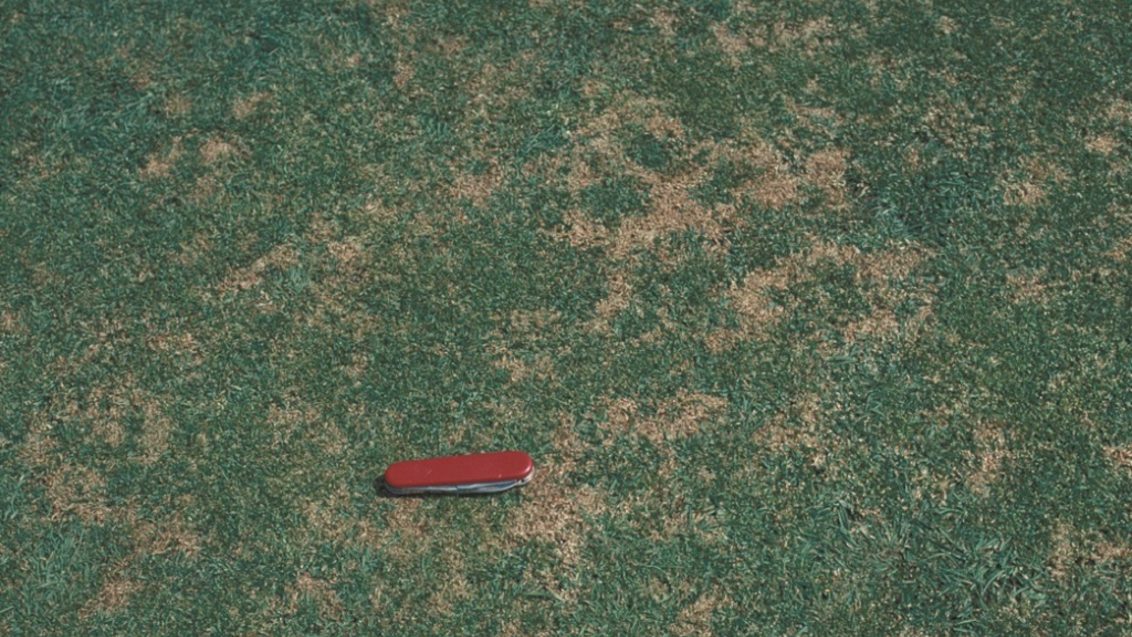
It causes irregularly shaped patches that are yellow to brown in color. Leaf lesions that are yellow with black centers may also occur. Anthracnose also causes a basal stem rot from late winter to fall. Infected shoots are easily detached. The dead foliage and stems also become covered with acervuli—tiny, spine, black fruiting bodies—that require magnification to identify.

Conditions Favoring Disease: Anthracnose favors temperatures over 26°C. It occurs in areas that experience more than 10 hours a day of leaf wetness for several consecutive days. Conditions that stress turfgrass plants, such as soil compaction, poor drainage, low mowing height, and low amounts of nitrogen fertility also contribute to this disease.
When is Anthracnose likely to attack turf?
Foliar blight is most common during hot, dry periods of the summer. Basal rot is mostly found during cool, wet weather from late autumn through winter and into early spring.
Effects of Anthracnose: Infection with Anthracnose reduces the playing quality of golf and bowling greens as the surface trueness is reduced. In severe cases (especially with foliar blight), loss of turf cover may occur, which may encourage the ingress of more Poa annua grass.
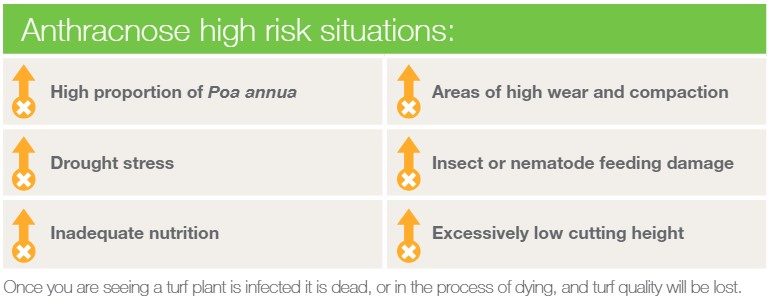
High Risk Situations: Presence of Poa annua.
Turfgrass that is under stress. Common stresses include drought conditions, compacted soils, areas of high wear, inadequate nitrogen, potassium or phosphorus, insect or nematode feeding, damage to grass plants caused by fungal pathogens and excessively low cutting heights.
Management Tips:
• Increase the height of cut.
• Minimize stress by using walk-behind mowers.
• Decrease the amount of foot traffic.
• Maintain adequate nitrogen and a balanced fertility level.
• Irrigate the turfgrass just enough to prevent wilting.
• Do not core aerate while disease symptoms are present.
• Core aerate and overseed in the fall.
• Convert from annual bluegrass to less susceptible varieties of turfgrass in the fairways.
• Make preventive fungicide applications where the disease is a chronic problem.
Fungicidal Control:
Preventative applications provide optimum control of anthracnose.
The following products have label recommendation for anthracnose control in the UAE:
|
Mode of action |
Systemic |
Systemic |
Systemic |
Protectant, Contact+ |
|
Dose rate |
3.2–6.4 l/ha OR 6.4–12.8 l/ha |
3–6 l/ha |
4.6–9.2 l/ha |
3.0 l/ha |
|
Water volume |
400 to 1000 l/ha |
400-800l/ha |
Refer to Product Label |
300-500 l/ha |
Labelled Products:





Anthracnose foliar blight
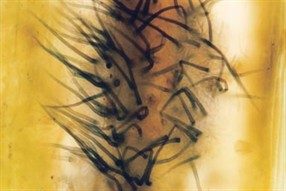
Acervulus with setae visible with a microscope.
Other Diseases in this category:







