Brown Patch
Turf Disease
What Is Brown Patch?
Brown patch is a disease that is caused by the pathogen Rhizoctonia solani. All turfgrass species are susceptible to its infection, but tall fescue and perennial ryegrass are most at risk. Tall fescue and ryegrass lawns in the transition zone, Mid-Atlantic, Midwest and Northeast can be exposed to brown patch under summer conditions with high humidity and night time temperatures above 20° C.

Causal Agent: Ceratorhiza cerealis (formerly Rhizoctonia cerealis)
Susceptible Turfgrass: Bentgrass, annual bluegrass, perennial ryegrass, bermudagrass
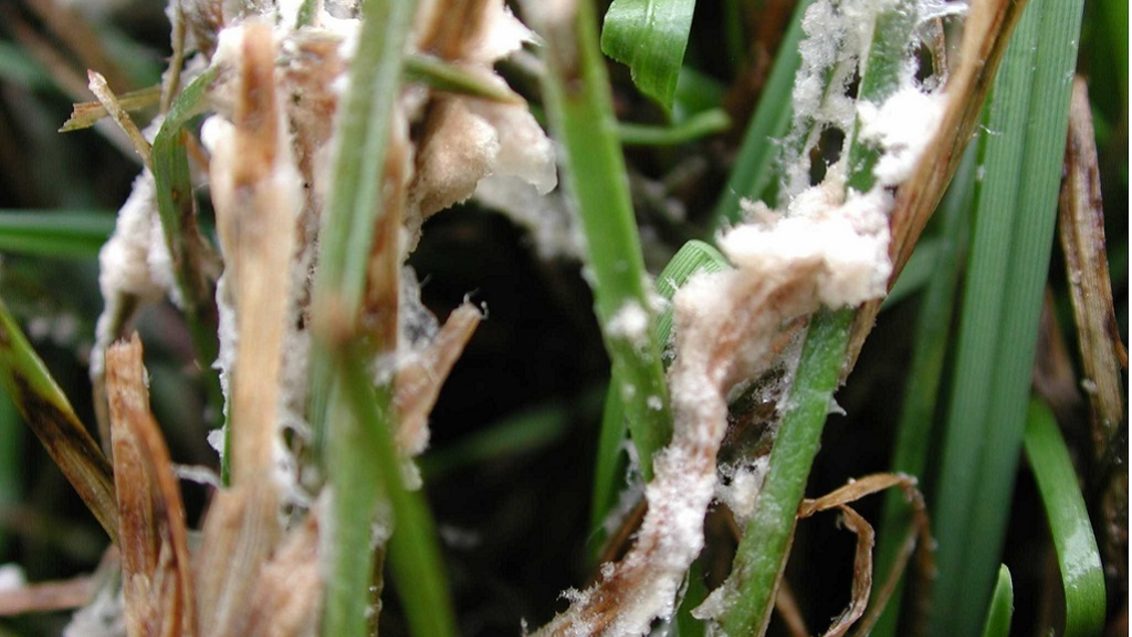
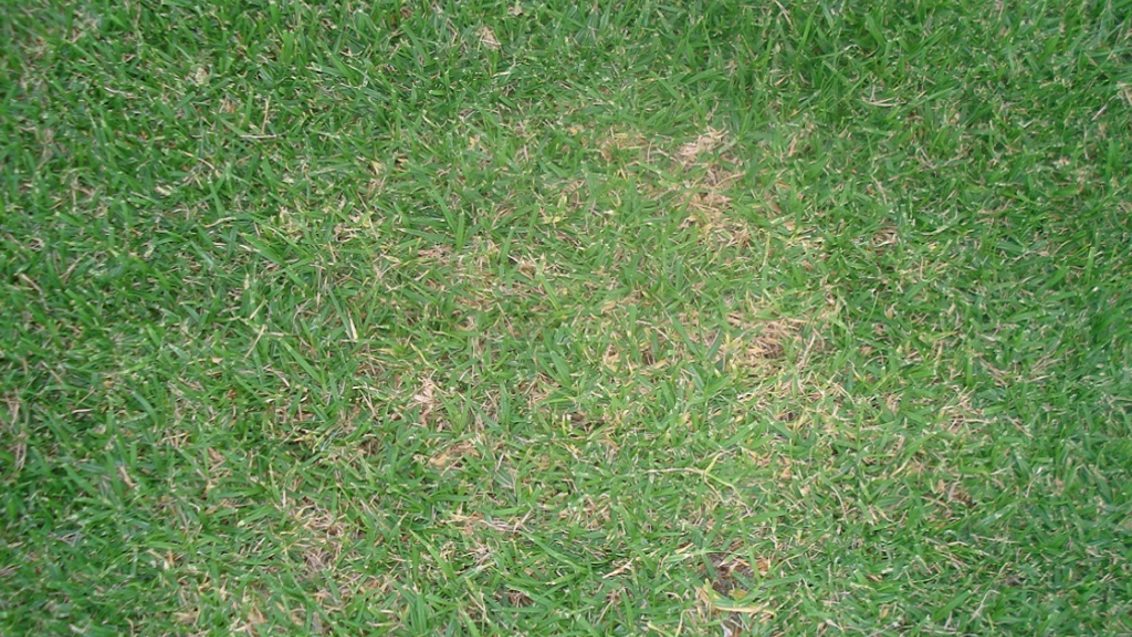
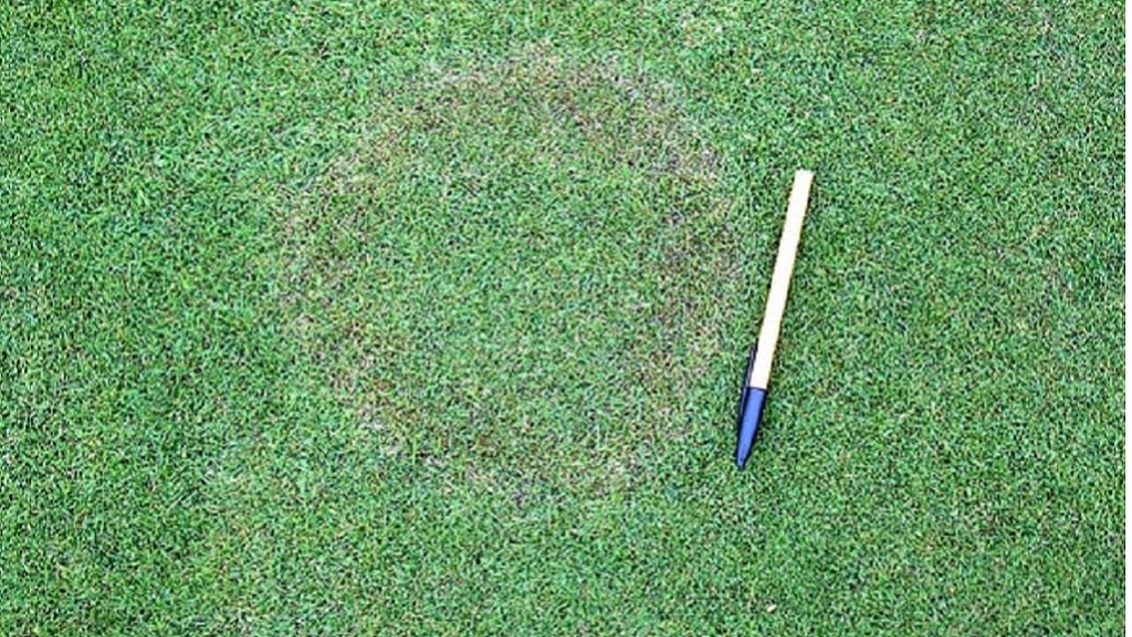
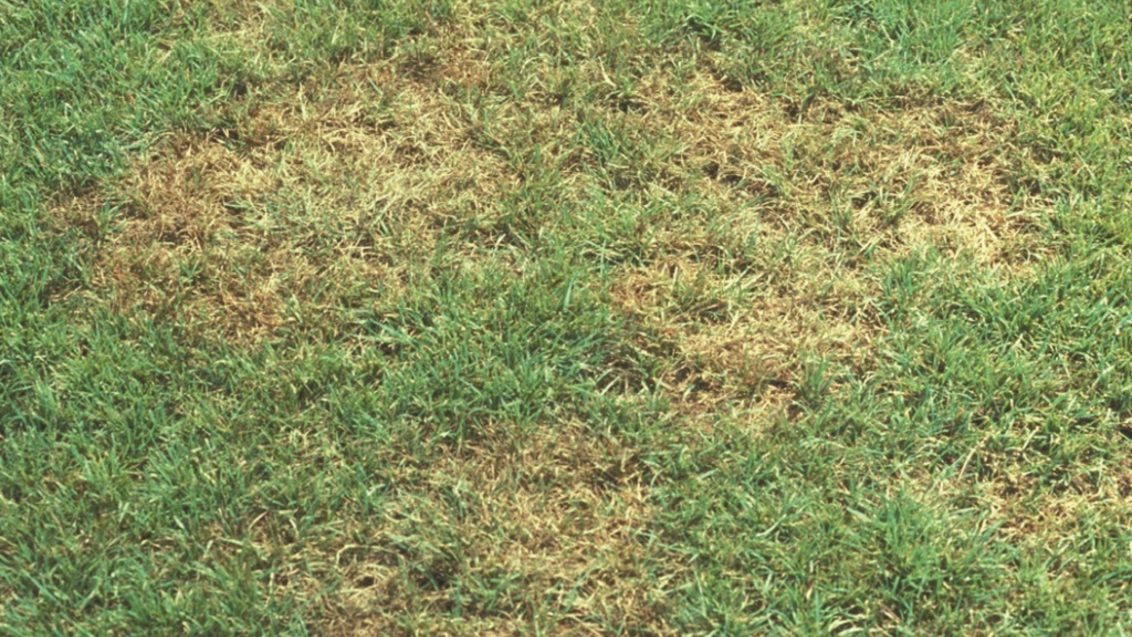
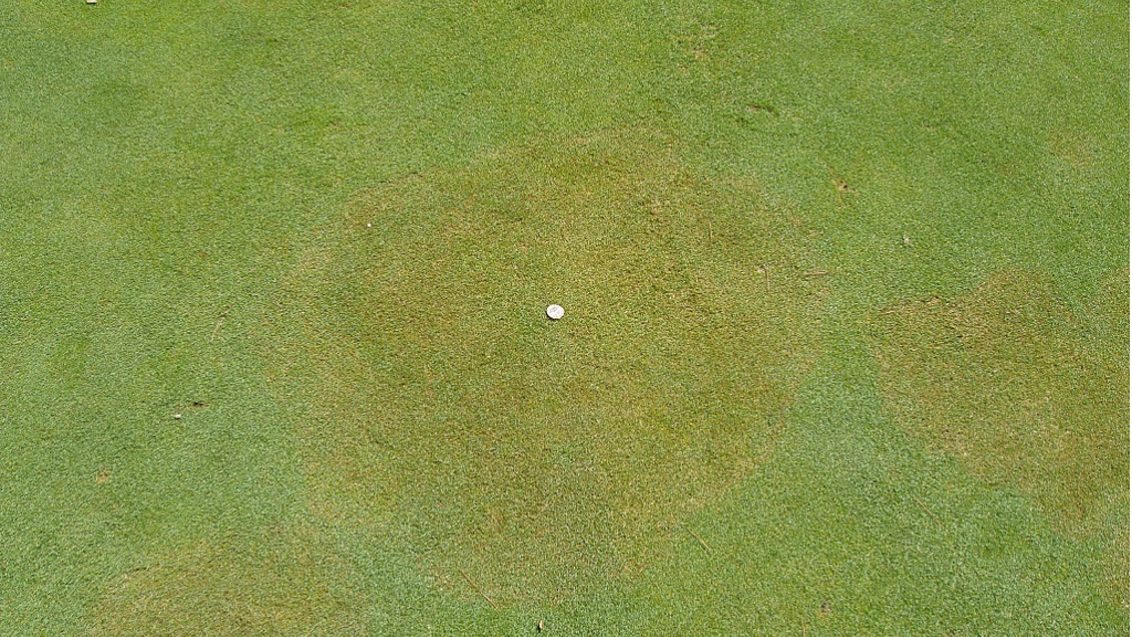
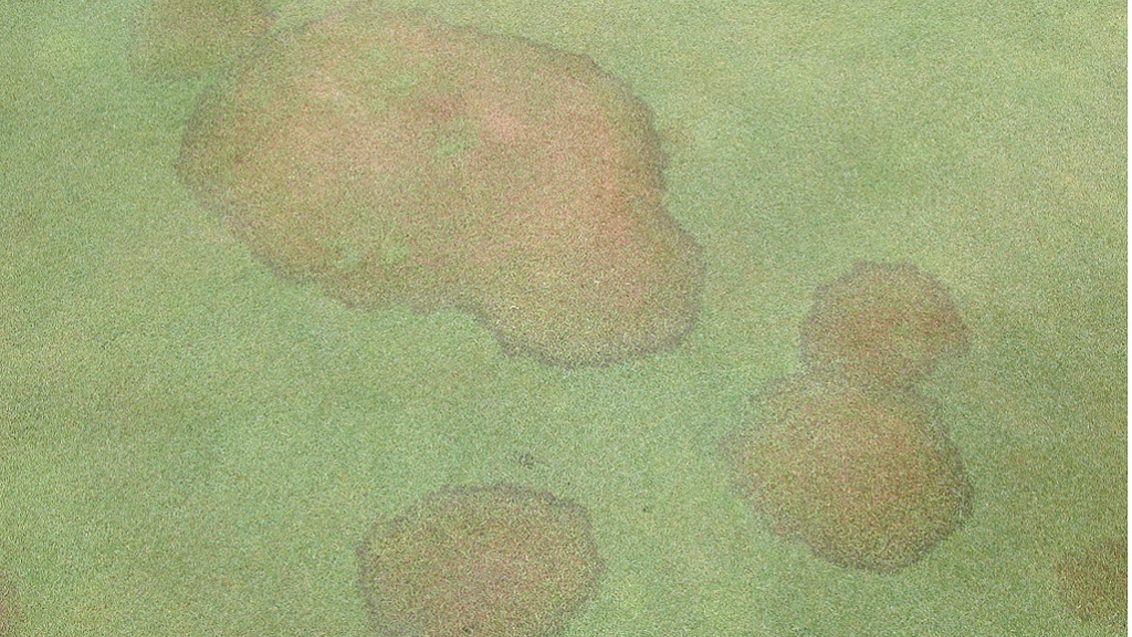
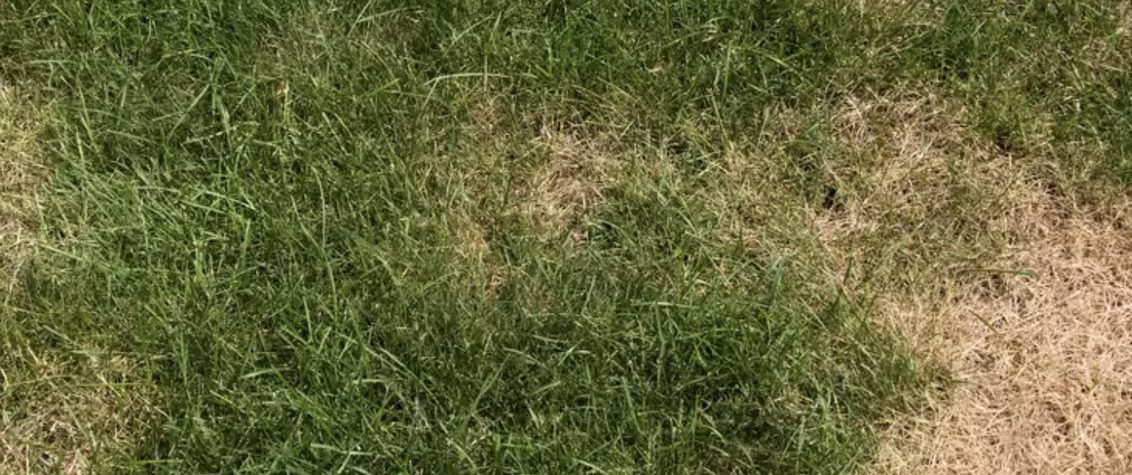
Symptoms: The symptoms of brown patch can vary depending on the grass cultivar, climatic and atmospheric conditions, soil, and intensity of the turfgrass management. This disease typically causes rings or patches of blighted turfgrass that measure 12 cm to more than 3 m in diameter. It also causes leaf spots and "smoke rings"-thin, brown borders around the diseased patches that appear most frequently in the early morning. After the leaves die in the blighted area, new leaves can emerge from the surviving crowns. On wide-bladed species, leaf lesions develop with tan centers and dark brown to black margins.
Conditions favoring Disease: Brown patch favors high relative humidity as well as temperatures of over 30°C during the day and over 15°C at night. This disease can be quite active at cool temperatures on warm-season grasses in the spring and autumn as temperatures in the turfgrass canopy, which is where infection starts, can often exceed air temperatures.
It also occurs in areas that experience more than 10 hours a day of foliar wetness for several consecutive days. Brown patch infestation is more severe when the turf is cut to a height less than the optimum for that turfgrass species.
When is Brown Patch likely to attack turf?
During the summer months, when the temperatures and humidity levels are high
Where is Brown Patch likely to attack?
Brown Patch is not very common but it is most frequently seen on close mown areas such as golf greens and bowling greens. On longer grass lesions may be found by close inspection but it is rare to encounter patches of disease.
Effects of Brown Patch: Brown Patch reduces the aesthetic appearance of the turf. In severe cases grass cover may be lost in the patches.
High Risk Situations:
- Temperatures over 20ºC.
- Leaf wetness or high humidity.
- Poor surface drainage.
- Excessive fertility.
Management Tips:
- Improve soil drainage.
- Use low to moderate amounts of nitrogen, moderate amounts of phosphorous, and moderate to high amounts of potash.
- Increase the air circulation.
- Minimize the amount of shade.
- Reduce thatch.
- Use contact or systemic fungicides preventively for best results
- Remove dew from turf early in the day
- Increase the height of cut
- Irrigate Turf Early in the day
Fungicidal Control:
Banner Maxx, Headway, Heritage Maxx, Medallion TL have a label recommendation for Brown Patch in UAE
|
|
||||
|
Mode of action |
Systemic |
Systemic |
Systemic |
Protectant, Contact+ |
|
Dose rate |
3.2–6.4 l/ha OR 6.4–12.8 l/ha |
3–6 l/ha |
4.6–9.2 l/ha |
3.0 l/ha |
|
Water volume |
400 to 1000 l/ha |
400-800l/ha |
Refer to Product Label |
300-500 l/ha |
Suggested Programme: Once conditions conducive to Brown Patch occur a preventative application of Banner Maxx should be applied.
Other Diseases in this category: